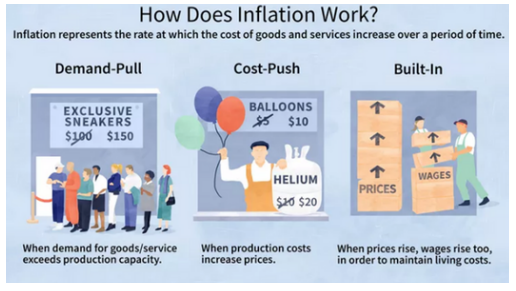
If you inflate a car/bike tyre or a balloon, it gets bigger. In finance, inflation is “the rate at which the price of goods and services rise”. High inflation can lead to a “loss in purchasing power” for consumers hence inflation is also understood as “a rise in prices, which can be translated as the decline of purchasing power over time”. In other words, the same amount of money will not buy as many goods or services. For example, if you saved up INR 100 to buy a school tiffin and inflation shot up by 10%, the exact same tiffin would cost INR 110 so now you would need an additional INR 10 to purchase it.
Normally inflation is either ‘demand pull’ or ‘cost push’. A ‘demand pull’ inflation occurs in case of increase in demand for products and services where as a ‘cost push’ inflation occurs as a result of increase in prices of raw materials/inputs used to produce a product or service. It can also be affected by factors like supply chain problems or political instability. If these issues make it hard for
sellers to obtain certain products or make it more expensive to produce them, then that drives up the price of those products.
In India the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) mainly seeks to control inflation. Their goal is to set policies that get the economy back to a stable balance between demand and supply so that prices do not continue to rise at a rapid rate.
T E S T Y O U R S E L F
Financial Terminology Knowledge
Match each statement with the right term.
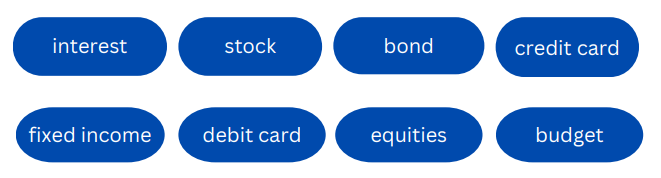
- A tool that helps you track your income and expenses to ensure that you are living within your means
- A card that allows you to make purchases by deducting money immediately and directly from your bank account.
- The fee you pay to borrow money.
- An investment that represents a share of ownership in a publicly traded company.
- An investment that represents a loan by an investor to a borrower
- A card that allows you to borrow money from a bank to make purchases and then pay that amount back at a later date plus lending fees
- Bonds are also called this term.
- Stocks are also called this term
What Do You Want to Learn About?
We want to answer your questions! After asking your parents’ permission, write to us at contactus@arthabodh.com and tell us the money questions and issues you would like to see covered in the next edition of Newsletter.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is the electronic version of the nation’s official currency and is issued by respective country’s central bank. In India, the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) will issue this legal tender, also known as the digital rupee .
- Digital Rupee (e₹) is a legal tender issued by the Reserve Bank of India in retail segment has components based on blockchain technology. Also called the “digital rupee” or e₹, it will offer features of physical cash like trust, safety and settlement finality with atomicity (i.e. immediate settlement of transactions) in digital mode.
- e₹ represents a direct claim on the central bank. It can be used to carry out transactions or store value digitally, similar to the manner in which currency notes can be used in physical form.
Some of the most obvious ways in which CBDC will impact common people include,
- Money transfers will be more efficient and will be settled faster
- Saving money for users since overall reduction in transaction costs for various money transfers including international money transfers as CBDC-based remittances will be quicker and cheaper
- 24X7 availability of transfer and remittance services
- Carrying and storage of physical cash, as well as the problem of
soiled and damaged notes, can be avoided.
How Digital Currency in India will Impact Its Economy:
- Faster and more efficient money transfers: Domestic and international money transfers are subject to various restrictions like turnaround times, bank holidays, weekends, etc. However, digital currency transactions will run at a high speed, 24/7, and transaction-related expenses is expected to be lower resulting into savings for the customers.
- Achieving Cashless Economy: Due to inclusion of the e-Rupee, more and more transactions will be cashless. Hence digital currency, or e-Rupee, will help the government achieve a cashless economy. A cashless economy means the convenience of digital transactions and freedom from the risk of carrying and storing cash
Money Fun Facts
Indian Rupee is made of cotton and not paper: Indian Rupee Notes are made up of
pulp which contains Cotton and Balsam with special dyes. India has been importing the special paper to be used in currencies for many years. There is a silk portion which is not publicised. The proportion of contents is secret. The purpose of using Cotton with Special Dyes is that the notes should be more resilient as well as durable. It will possess a quality to resist from wear and tear and it won’t be so easy to fake it.